Same as the coil used in the previous notes. The Inductor is a coiled conductor usually a copper wire. An Inductor connected across a DC voltage source from the circuit below has a current flow across the Inductor coil. This generates a Magnetic field around the Coil.
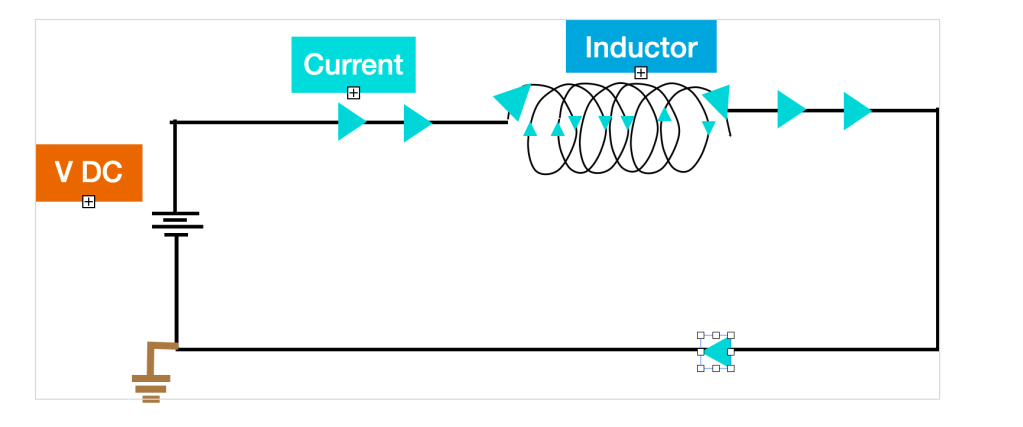
This generated Magnetic field forces the current from changing in the circuit even with a short voltage supply. “Emil Lenz” determined this phenomenon and called it Lenz Law.
The direction of the Magnetic field and Current are as shown below, determined by the right-Hand Rule where the thumb points the direction of the current and the folded fingers point the direction of the Magnetic Field. Inductors store current in the form of a Magnetic Field.
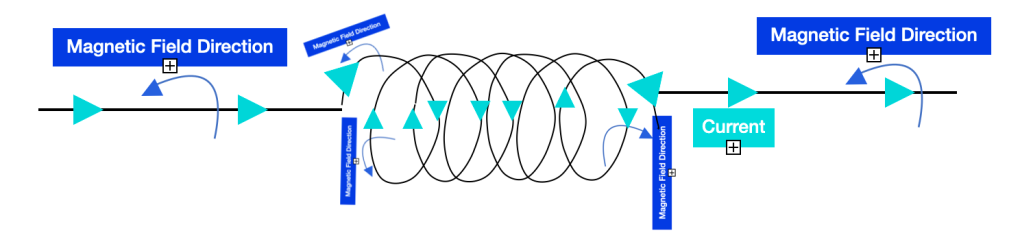
The Inductor maintains a constant flow of current through it. Generated Magnetic field forces this to happen.
Circuit with a Switch:

From the circuit even when the Voltage source is OFF the current still flows in the circuit due to the inductor. For an ideal wire with “0” Resistance, the current flow forever in the loop. In a real case, the duration of the current flow depends on the resistance of the wire and the inductance of the Inductor. Even when the voltage terminates, the LED still glows momentarily. The Inductor acts like a normal short cable in a steady state condition.

No matter what the resistance on the cable is, the inductor will force to maintain the current, be it for a concise time. This generates very high voltages when the connected Resistor has a very high Resistance. This explains the usage of inductors in the high voltage generating circuits like “Boost converters”.
The inductance of an Inductor increases with increase in N- Number of turns or A- Area of the coil or Permeability of the core and decreases with increase in l- Average length of the coil.

L : Inductance (Henry, H)
N: Number of turns
u: Permeability of the core
l: Average length of the coil
A: Area of the coil
As the Inductance (L) increases the Voltage (v) across will increase. The relation between L and v is as below, Voltage is the Inductance (L) times the rate of change of Current (di/dt).
Impedance value of the Inductor.